Catalogue of traps and pheromones
Download traps and pheromones list

Download document
1.02 mb
Pink bollworm is an insect known for being a pest in cotton farming.
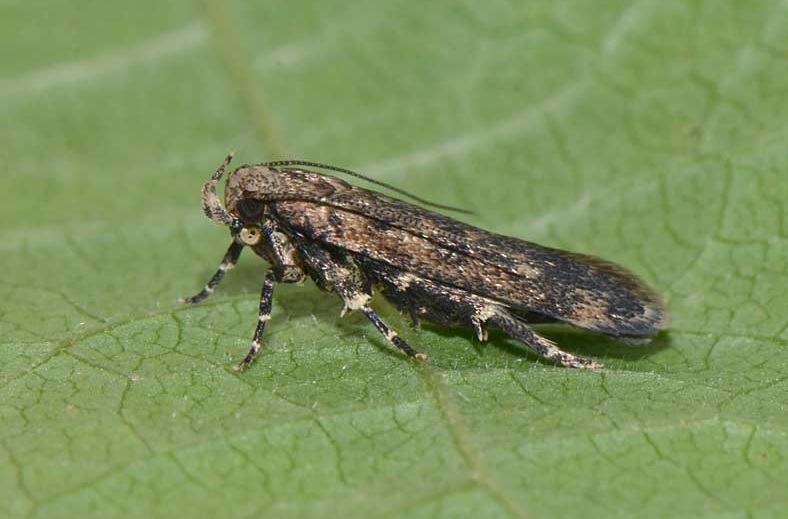

Infestation on susceptible cotton is generally controlled with insecticides. Biochemtech S.R.L. offer the solution of pest control management which can be used without any harm for pollinators, human being, pollution – the solution which can prevent damages and grow the harvest.

Once a crop has been harvested, the field is plowed under as soon as possible to stop the life cycle of the new generation of pink bollworm. Unharvested bolls harbor the larvae, so these are destroyed. The plants are plowed into the earth and the fields are irrigated liberally to drown out remaining pests. Some farmers burn the stubble after harvest. Surviving bollworms will overwinter in the field and re-infest the following season.
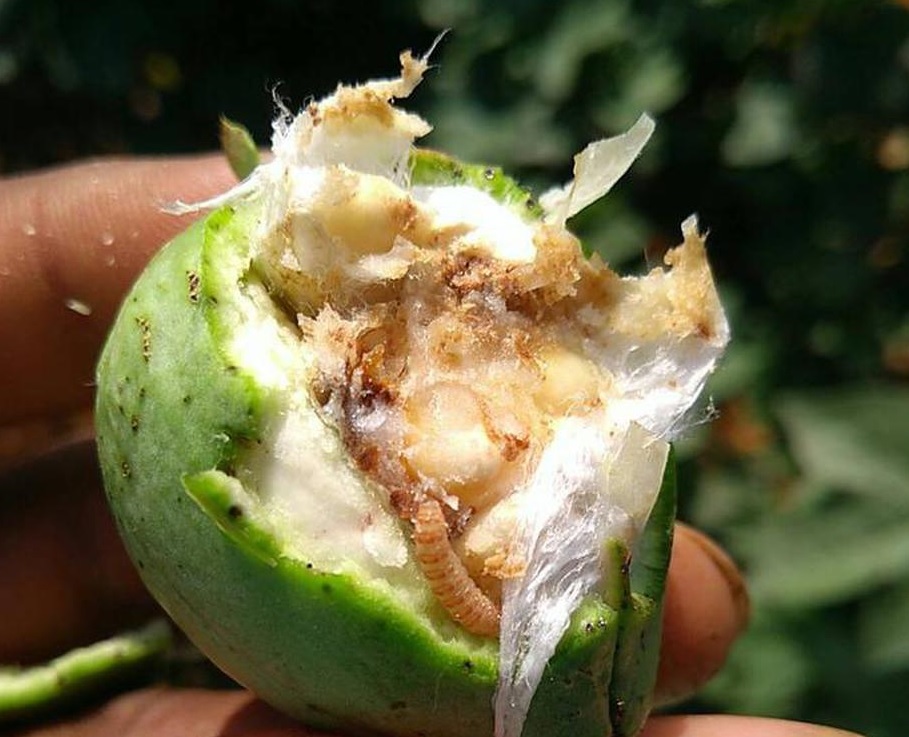
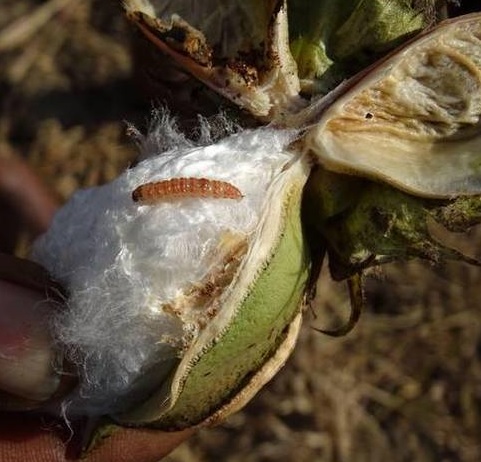



Pink bollworm causes failure of buds to open, fruit shedding, lint damage and seed loss. Pink bollworm is a worldwide pest of cotton and in some regions of the world, it is the key cotton pest.
Female are usually laid singly, or in groups of 5-10. Pink bollworm eggs are deposited on or near the cotton bolls at the time of flowering.
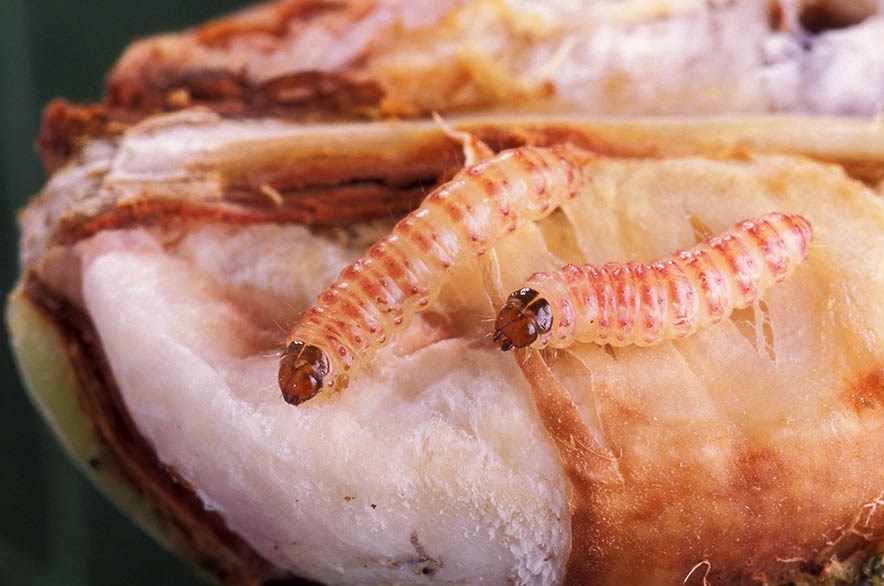


Young larvae emerge after 3-5 days (in optimum conditions), entering the cotton bolls shortly after emergence where they feed internally within the pod, making a small hole to the exterior to allow air to penetrate. Larvae usually pass through four instars. Pupation takes place in the ground, about 50 mm below the surface and adults emerge after about 9 days. Adults are nocturnal and females begin laying eggs a day or two after emergence, typically laying 200-400 eggs each.
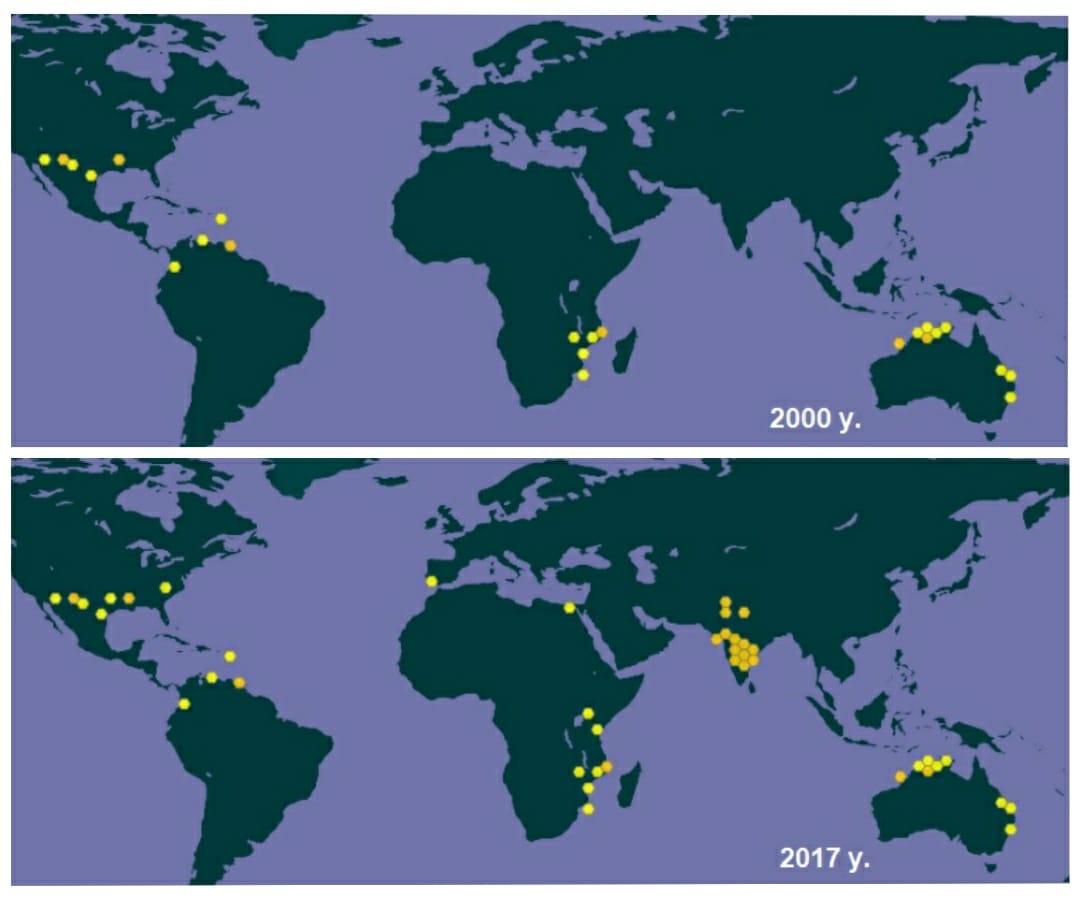
Pink bollworm is distributed throughout tropical America, Africa, Asia, Australasia, including subtropical regions, Pakistan, Egypt and Mexico. Pink bollworm is a quarantine pest in the USA and Russia.
SYNONYM:
Depressaria gossypiella
Ephestia gossypiella
Gelechia gossypiella
Gelechiella gossypiella
Platyedra gossypiella
Proper use of Pheromone Traps:
The pheromone trap is designed to monitor and reduce pest numbers. In order to determine the population density of pest insects and to identify pest outbreaks (monitoring), it is recommended to use 1 trap per 1 ha.
The trap should be placed in the crown of the tree at a height of 1.5-2 m. Prior to the first flight of the butterflies, the traps must be checked on a daily basis, and after the first butterflies have been captured, the traps must be checked every 5-7 days. Pheromone dispensers and adhesive tapes can be replaced as needed. Protective measures are based on the results of the monitoring of population density of pest insects.
Trap placement:
For mass capture and sterilization of males, it is recommended to have more than 20 traps per hectare. In case of a large number of pest insects use 30 traps per 1 ha.


Download traps and pheromones list

1.02 mb
Review our catalogue of pheromons and semiochemicals by chemical name

525.1 kb