Catalogue of traps and pheromones
Download traps and pheromones list

Download document
1.02 mb
The Cotton bollworm attacks more than 120 plant species: corn, cotton, tomatoes, tobacco, chickpeas, sorghum, okra, pumpkin, zucchini, soy, castor, sesame, hemp, peas, kenaf, jute, rope, alfalfa, pepper, cabbage, beans, onion, peanuts, sunflower, flax, Apple, pear, plum, peach, mango, citrus, geranium, clove, lemon eucalyptus, verbena etc. The caterpillars attack all the ground vegetative organs of plants.

The larva can destroy 10 to 24 fruit organs during its evolution. Young caterpillars skeletonize leaf blades, buds, and young cotton pods. Older caterpillars eat buds, leaves, ovaries, gnaw out grains in boxes.
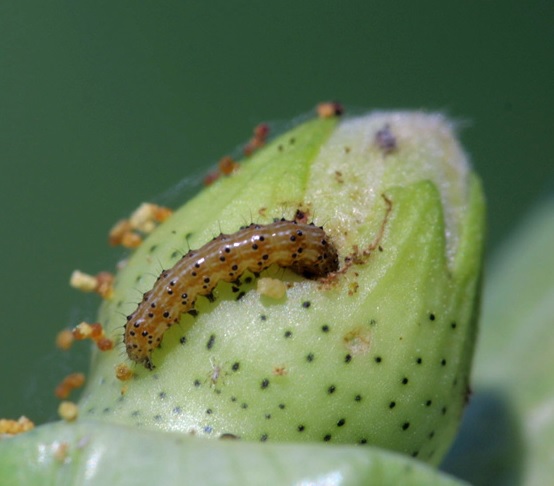

The Cotton bollworm flight begins at an average daily temperature of + 18°C – +20 °C. In Central Asia, the first butterflies appear in April-early may. In Azerbaijan-in mid-may. In Ukraine, in mid-June and summer lasts until October-November. To complete their development, they need additional nutrition on flowering vegetation.

After several days of feeding, copulation and egg laying occur, processes that occur during the night. The female can lay 500 to 1500 eggs or even more. They are deposited isolated or in groups under the foliage.
Proper use of Pheromone Traps:
The pheromone trap is designed to monitor and reduce pest numbers. In order to determine the population density of pest insects and to identify pest outbreaks (monitoring), it is recommended to use 1 trap per 1 ha.
The trap should be placed in the crown of the tree at a height of 1.5-2 m. Prior to the first flight of the butterflies, the traps must be checked on a daily basis, and after the first butterflies have been captured, the traps must be checked every 5-7 days. Pheromone dispensers and adhesive tapes can be replaced as needed. Protective measures are based on the results of the monitoring of population density of pest insects.
Trap placement:
For mass capture and sterilization of males, it is recommended to have more than 20 traps per hectare. In case of a large number of pest insects use 30 traps per 1 ha.

Download traps and pheromones list

1.02 mb
Review our catalogue of pheromons and semiochemicals by chemical name

525.1 kb